Zone-Based Approach To Implementing Data-Centric Security
When viewing scoping, there are nine (9) zones for sensitive data compliance purpose.
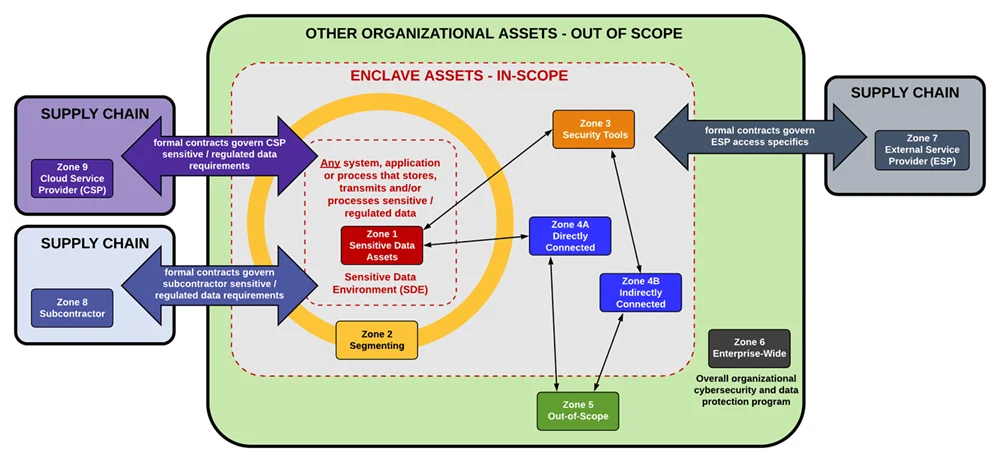
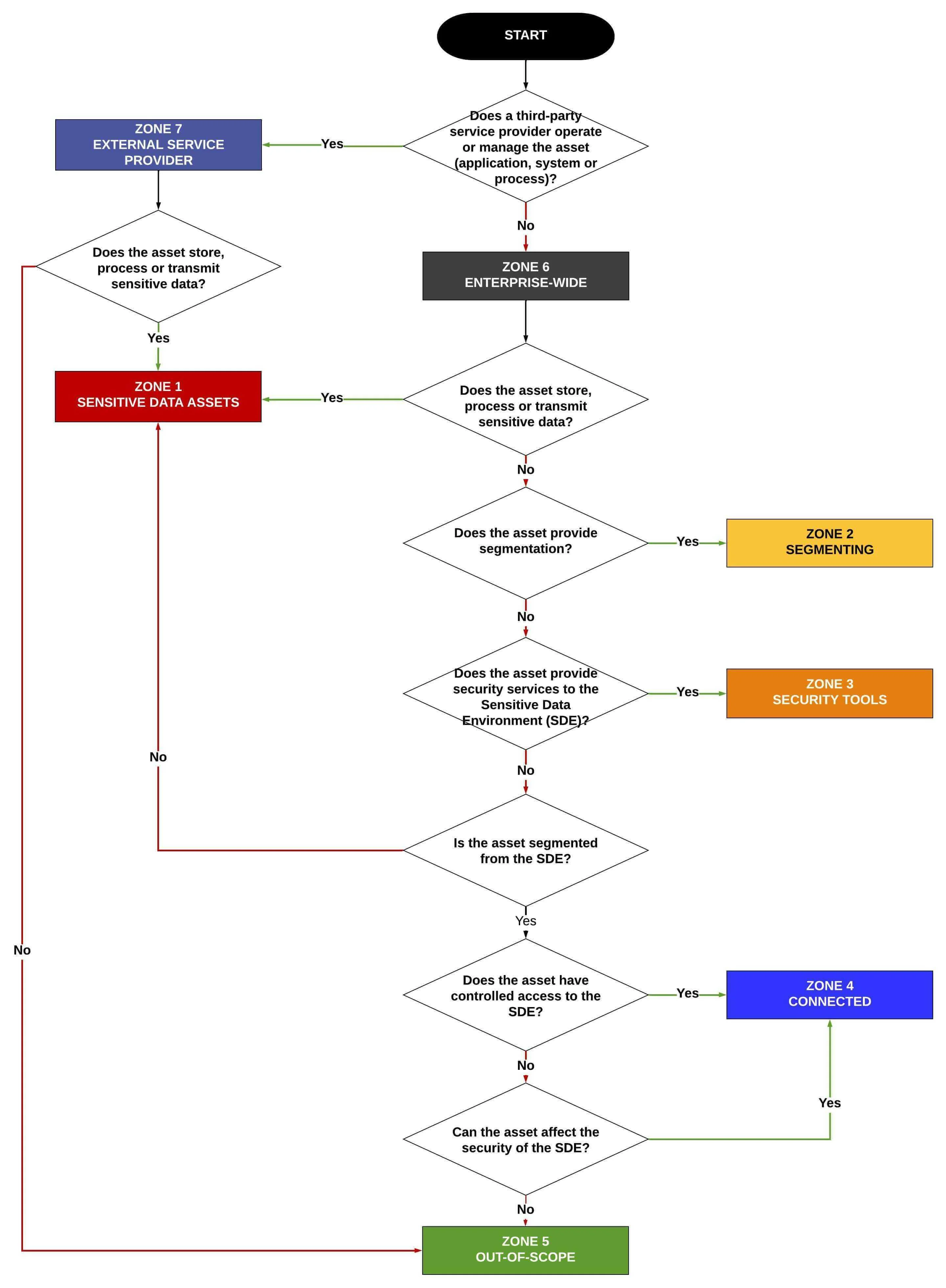
- Sensitive Data Assets: The first zone contains systems, services and applications that directly store, transmit and/or process sensitive data.
- Segmenting: The second zone contains “segmenting systems” that provide access (e.g., firewall, hypervisors, etc.).
- Security Tools: The third zone contains “security tools” that directly impact the integrity of category 1 and 2 assets (e.g., Active Directory, centralized antimalware, vulnerability scanners, IPS/IDS, etc.).
- Connected. The fourth zone contains connected systems. These are systems, embedded technologies, applications or services that have some direct or indirect connection into the sensitive data environment. Systems, embedded technologies, applications and services that may impact the security of (for example, name resolution or web redirection servers) the sensitive data environment are always in scope. Essentially, it something can impact the security of sensitive data, it is in scope.
- Out-of-Scope. The fifth zone contains out-of-scope systems that are completely isolated from the sensitive data systems.
- Enterprise-Wide. The sixth zone addresses the organization’s overall corporate security program (cyber and physical).
- External Service Provider. The seventh zone addresses supply-chain security with the “flow down” of contractual requirements to External Service Providers (ESPs) that can directly or indirectly influence the sensitive data environment. ESPs are third-party organizations that provide services to the organizations.
- Subcontractors. The eighth zone addresses subcontractors, which are third-party organizations that are party to the actual execution of the contract where the subcontractor may create, access, receive, store and/or transmit regulated data (sensitive data).
- Cloud Service Provider. The nineth zone addresses CSPs, which are a specialized form of ESP. An ESP is a CSP when it offers “cloud computing services” that enable ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction
Zone 1: All systems, applications and services that store, transmit and/or process sensitive data are Category 1 devices. These systems that interact with sensitive data are the main assets that sensitive data are trying to protect
Zone 2: All network devices or hypervisors that provide segmentation functions are Category 2 devices. This category involves systems that provide segmentation and prevent "sensitive data contamination" from the sensitive data environment to uncontrolled environments. Typically, these are firewalls or segmentation technology that implement some form of Access Control List (ACL) to restrict logical access into and out of the sensitive data environment. This can also include Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) components that provide micro-segmentation services
Note: If network segmentation is in place and is being used to reduce the scope of an assessment, expect the assessor to verify that the segmentation is adequate to reduce the scope of the assessment. the more detailed the documentation your assessor will require to adequately review the implemented segmenting solution.
Zone 3: All systems that provide security-related services or IT-enabling services that may affect the security of the sensitive data environment are Category 3 devices. There are systems that can impact configurations, security services, logging, etc. that can be in a dedicated security subnet or on the corporate LAN.
These include, at a minimum:
- Identity and Directory Services (Active Directory, LDAP);
- Domain Name Systems (DNS);
- Network Time Systems (NTP);
- Patch management systems;
- Vulnerability & patch management systems;
- Anti-malware management systems;
- File Integrity Management (FIM) systems;
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) systems;
- Performance monitoring systems;
- Cryptographic key management systems;
- Remote-access or Virtual Private Network (VPN) systems;
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) systems;
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) systems;
- Log management and Security Incident Event Management (SIEM) systems; and
- Intrusion Detection Systems/ Intrusion Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS).
Zone 4: Any system that has some capability to communicate with systems, applications or services within the sensitive data environment is a Category 4 device. A “connected” system, embedded technologies, application or service should be considered in scope for since it is not completely isolated. If it can potentially impact the security of sensitive data, it is in scope.
There are two sub-categories of connected devices:
- Directly Connected; and
- Indirectly Connected.
Zone 4A: This sub-category addresses any system that is “connected to” the sensitive data environment is considered a directly-connected system. Any system outside of the sensitive data environment that is capable of communicating with a system that stores, transmits or processes sensitive data (e.g., asset within the sensitive data environment) is a Category 4A device.
Note: For systems outside of the sensitive data environment that have periodic controlled and managed outbound connections from the sensitive data environment that do not involve the transfer of regulated data (sensitive data), there is a case to argue that the system could be ruled out-of-scope since it cannot have an impact on the security of sensitive data. In cases like this, some form of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tool may be warranted to act as a compensating control to further demonstrate how the asset would be out-of-scope.
Zone 4B: This sub-category addresses any system that does not have any direct access to sensitive data systems (e.g., not interacting with the sensitive data environment). Any system that has access to Connected or Segmenting systems and that could affect the security of the sensitive data environment is a Category 4B device.
An example of an indirectly connected system would be that of an administrator's workstation that can administer a security device (Active Directory, firewall, etc.) or upstream system that feeds information to connected systems (e.g. patching system, DNS, etc.). In the case of a user directory, an administrator could potentially grant himself/herself (or others) rights to systems in the sensitive data environment, therefore breaching the security controls applicable to the sensitive data environment.
Zone 5: Any system, application or service that is not a sensitive data-contaminated, segmenting or connected system is a Category 5 asset. These assets are considered out-of-scope for sensitive data. These out-of-scope assets must be completely isolated (no connections whatsoever) from sensitive data systems, though they may interact with connected systems (and can even reside in the same network zone with connected systems).
Four (4) tests must be considered to confirm that a system is out-of-scope and considered a Category 5 asset. This amounts to ensuring that the asset does not fall under the previously defined categories:
- System components do NOT store, process, or transmit sensitive data.
- System components are NOT on the same network segment or in the same subnet or VLAN as systems, applications or processes that store, process, or transmit sensitive data.
- System component cannot connect to or access any system in the sensitive data environment.
- System component cannot gain access to the sensitive data environment, nor impact a security control for a system, embedded technologies, application or service in the sensitive data environment via an in-scope system.
Zone 6: This category addresses enterprise-wide security controls that exist outside of just the sensitive data environment. Within this category are the corporate-wide security practices that affect both cyber and physical security, including security-related policies, standards and procedures that affect the entire organization.
Zone 7: Sensitive data in the supply chain needs to be taken seriously and this category addresses External Service Providers (ESPs). The formal contracts between your organization its ESPs dictate the logical and physical access those ESP have to the organization’s facilities, systems and data. The “flow down” considerations of sensitive data must be addressed with each ESP to clearly identify the ESPs’ ability to directly or indirectly influence the sensitive data environment.
Examples of ESPs that may have sensitive data flow down requirements:
- Bookkeepers;
- Human Resource (HR) recruiters;
- Payroll providers;
- Educational training providers;
- IT service providers / cybersecurity consultants / Managed Service Provider (MSP);
- Business process consultants;
- Project Managers (PMs);
- Document destruction providers; and
- Janitorial services and environmental control management.
Zone 8: This category addresses subcontractors necessary to perform the in-scope contract. While a subcontractor is a third-party, a subcontractor is party to the actual execution of the contract where the subcontractor may create, access, receive, store and/or transmit sensitive data.
Zone 9: This category addresses ESP providing cloud computing services that enable ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. A CSP can be identified by its function, since the cloud model is composed of five (5) essential characteristics, three (3) service models and four (4) deployment models:
Essential Characteristics:
- On-demand self-service;
- Broad network access;
- Resource pooling;
- Rapid elasticity; and
- Measured service.
Service Models:
- Software as a Service (SaaS);
- Platform as a Service (PaaS); and
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
Deployment Models:
- Private cloud;
- Community cloud;
- Public cloud; and
- Hybrid cloud.
Scoping Is A Due Diligence Activity








