Policy
# |
DSP Policy |
Identifier |
DSP Policy Intent |
| 1 |
Security & Privacy Governance |
GOV |
The GOV policy is focused on helping an organization specify the development of an organization’s security and privacy programs, including criteria to measure success, to ensure ongoing leadership engagement and risk management. |
| 2 |
Artificial Intelligence & Autonomous Technologies |
AAT |
The AAT policy is focused on ensuring trustworthy and resilient Artificial Intelligence (AI) and autonomous technologies to achieve a beneficial impact by informing, advising or simplifying tasks. |
| 3 |
Asset Management |
AST |
The AST policy is focused on helping an organization ensure technology assets are properly managed throughout the lifecycle of the asset, from procurement through disposal, ensuring only authorized devices are allowed to access the organization’s network and to protect the organization’s data that is stored, processed or transmitted on its assets. |
| 4 |
Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery |
BCD |
The BCD policy is focused on helping an organization establish processes that will help the organization recover from adverse situations with the minimal impact to operations, as well as provide the ability for e-discovery. |
| 5 |
Capacity & Performance Planning |
CAP |
The CAP policy is focused on helping an organization prevent avoidable business interruptions caused by capacity and performance limitations by proactively planning for growth and forecasting, as well as requiring both technology and business leadership to maintain situational awareness of current and future performance. |
| 6 |
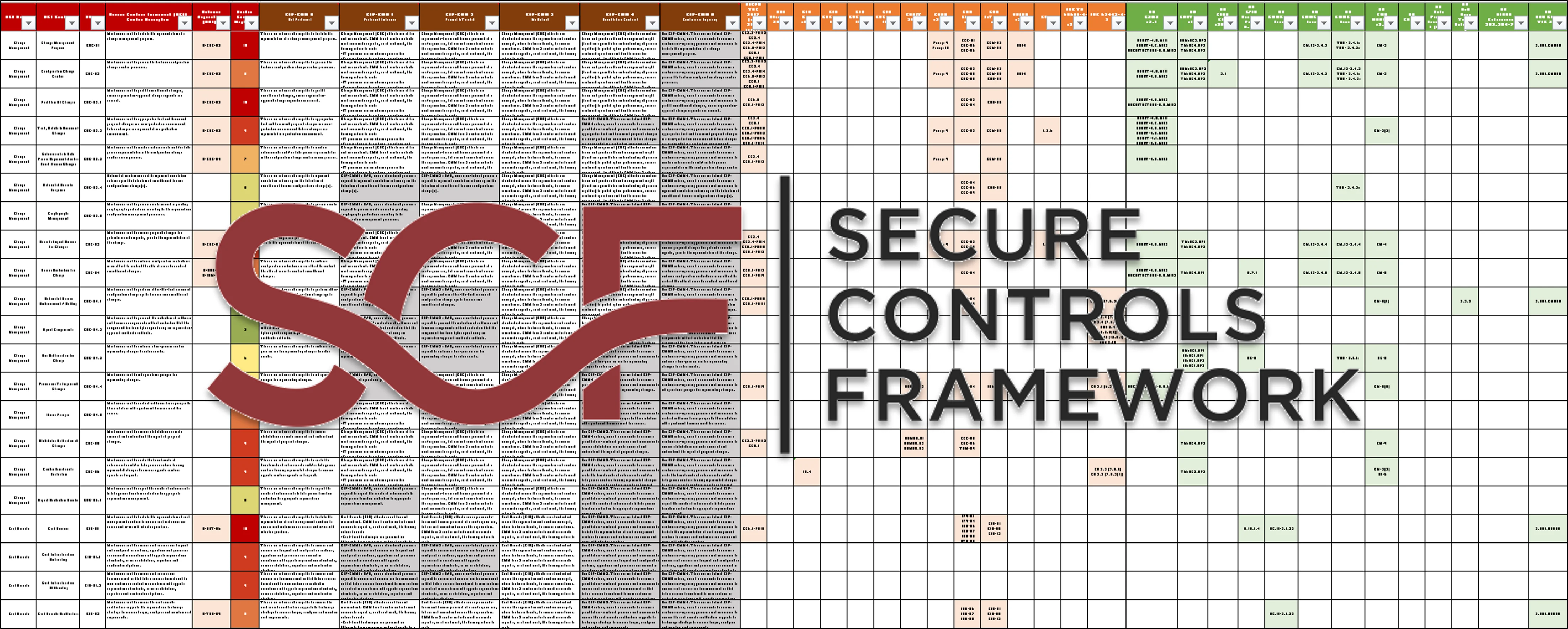
Change Management |
CHG |
The CHG policy is focused on helping an organization ensure both technology and business leadership proactively manage change. This includes the assessment, authorization and monitoring of technical changes across the enterprise so as to not impact production systems uptime, as well as allow easier troubleshooting of issues. |
| 7 |
Cloud Security |
CLD |
The CLD policy is focused on helping an organization govern the use of private and public cloud environments (e.g., IaaS, PaaS and SaaS) to holistically manage risks associated with third-party involvement and architectural decisions, as well as to ensure the portability of data to change cloud providers, if needed. |
| 8 |
Compliance |
CPL |
The CPL policy is focused on helping an organization ensure controls are in place to be aware of and comply with applicable statutory, regulatory and contractual compliance obligations, as well as internal company standards. |
| 9 |
Configuration Management |
CFG |
The CFG policy is focused on helping an organization establish and maintain the integrity of systems. Without properly documented and implemented configuration management controls, security features can be inadvertently or deliberately omitted or rendered inoperable, allowing processing irregularities to occur or the execution of malicious code. |
| 10 |
Continuous Monitoring |
MON |
The MON policy is focused on helping an organization establish and maintain ongoing situational awareness across the enterprise through the centralized collection and review of security-related event logs. Without comprehensive visibility into infrastructure, operating system, database, application and other logs, the organization will have “blind spots” in its situational awareness that could lead to system compromise, data exfiltration, or unavailability of needed computing resources. |
| 11 |
Cryptographic Protections |
CRY |
The CRY policy is focused on helping an organization ensure the confidentiality of the organization’s data through implementing appropriate cryptographic technologies to protect systems and data. |
| 12 |
Data Classification & Handling |
DCH |
The DCH policy is focused on helping an organization ensure that technology assets, both hardware and media, are properly classified and measures implemented to protect the organization’s data from unauthorized disclosure, regardless if it is being transmitted or stored. Applicable statutory, regulatory and contractual compliance requirements dictate the minimum safeguards that must be in place to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data. |
| 13 |
Embedded Technology |
EMB |
The EMB policy is focused on helping an organization specify the development, proactive management and ongoing review of security embedded technologies, including hardening of the “stack” from the hardware, to firmware, software, transmission and service protocols used for Internet of Things (IoT) and Operational Technology (OT) devices. |
| 14 |
Endpoint Security |
END |
The END policy is focused on helping an organization ensure that endpoint devices are appropriately protected from security threats to the device and its data. Applicable statutory, regulatory and contractual compliance requirements dictate the minimum safeguards that must be in place to protect the confidentiality, integrity, availability and safety considerations. |
| 15 |
Human Resources Security |
HRS |
The HRS policy is focused on helping an organization create a security and privacy-minded workforce and an environment that is conducive to innovation, considering issues such as culture, reward and collaboration. |
| 16 |
Identification & Authentication |
IAC |
The IAC policy is focused on helping an organization implement the concept of “least privilege” through limiting access to the organization’s systems and data to authorized users only. |
| 17 |
Incident Response |
IRO |
The IRO policy is focused on helping an organization establish and maintain a capability to guide the organization’s response when security or privacy-related incidents occur and to train users how to detect and report potential incidents. |
| 18 |
Information Assurance |
IAO |
The IAO policy is focused on helping an organization ensure the adequately of security and controls are appropriate in both development and production environments. |
| 19 |
Maintenance |
MNT |
The MNT policy is focused on helping an organization ensure that technology assets are properly maintained to ensure continued performance and effectiveness. Maintenance processes apply additional scrutiny to the security of end-of-life or unsupported assets. |
| 20 |
Mobile Device Management |
MDM |
The MDM policy is focused on helping an organization govern risks associated with mobile devices, regardless if the device is owned by the organization, its users or trusted third-parties. Wherever possible, technologies are employed to centrally manage mobile device access and data storage practices. |
| 21 |
Network Security |
NET |
The NET policy is focused on helping an organization ensure sufficient security and privacy controls are architected to protect the confidentiality, integrity, availability and safety of the organization’s network infrastructure, as well as to provide situational awareness of activity on the organization’s networks. |
| 22 |
Physical & Environmental Security |
PES |
The PES policy is focused on helping an organization minimize physical access to the organization’s systems and data by addressing applicable physical security controls and ensuring that appropriate environmental controls are in place and continuously monitored to ensure equipment does not fail due to environmental threats. |
| 23 |
Privacy |
PRI |
The PRI policy is focused on helping an organization align privacy engineering decisions with the organization’s overall privacy strategy and industry-recognized leading practices to secure Personal Information (PI) that implements the concept of privacy by design and by default. |
| 24 |
Project & Resource Management |
PRM |
The PRM policy is focused on helping an organization ensure that security-related projects have both resource and project/program management support to ensure successful project execution. |
| 25 |
Risk Management |
RSK |
The RSK policy is focused on helping an organization ensure that security and privacy-related risks are visible to and understood by the business unit(s) that own the assets and / or processes involved. The security and privacy teams only advise and educate on risk management matters, while it is the business units and other key stakeholders who ultimately own the risk. |
| 26 |
Secure Engineering & Architecture |
SEA |
The SEA policy is focused on helping an organization align cybersecurity engineering and architecture decisions with the organization’s overall technology architectural strategy and industry-recognized leading practices to secure networked environments. |
| 27 |
Security Operations |
OPS |
The OPS policy is focused on helping an organization ensure appropriate resources and a management structure exists to enable the service delivery of cybersecurity operations. |
| 28 |
Security Awareness & Training |
SAT |
The SAT policy is focused on helping an organization develop a security and privacy-minded workforce through continuous education activities and practical exercises, in order to refine and improve on existing training. |
| 29 |
Technology Development & Acquisition |
TDA |
The TDA policy is focused on helping an organization ensure that security and privacy principles are implemented into any products/solutions that are either developed internally or acquired to make sure that the concepts of “least privilege” and “least functionality” are incorporated. |
| 30 |
Third-Party Management |
TPM |
The TPM policy is focused on helping an organization ensure that security and privacy risks associated with third-parties are minimized and enable measures to sustain operations should a third-party become defunct. |
| 31 |
Threat Management |
THR |
The THR policy is focused on helping an organization establish a capability to proactively identify and manage technology-related threats to the security and privacy of the organization’s systems, data and business processes. |
| 32 |
Vulnerability & Patch Management |
VPM |
The VPM policy is focused on helping an organization proactively manage the risks associated with technical vulnerability management that includes ensuring good patch and change management practices are utilized. |
| 33 |
Web Security |
WEB |
The WEB policy is focused on helping an organization address the risks associated with Internet-accessible technologies by hardening devices, monitoring system file integrity, enabling auditing, and monitoring for malicious activities. |